The Influence of Elders in Historical Somaliland
In the historical context of Somaliland, elders have been indispensable figures in maintaining the societal framework. Their roles have spanned from safeguarding cultural traditions to overseeing community governance. Over the years, their contributions have been essential in ensuring social harmony, mediating conflicts, and transmitting values from one generation to the next. By exploring the multifaceted roles they played, we can gain a deeper understanding of their substantial influence on the socio-political landscape of the region.
The Structure of Eldership
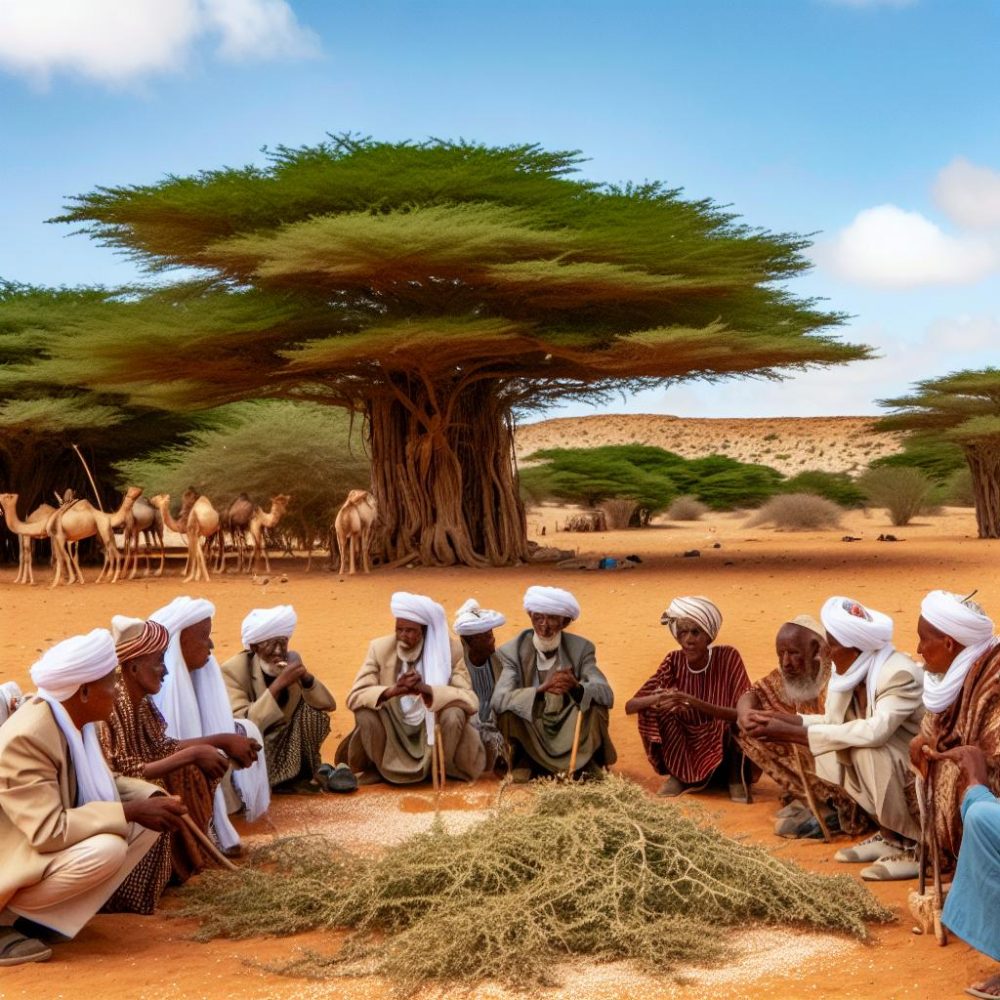
The traditional societal structure of Somaliland is predominantly clan-based, with each clan holding significant autonomy under the leadership of elders. These individuals are esteemed for their wisdom and experience, characteristics that form the bedrock of their leadership roles. In Somali culture, seniority naturally intertwines with authority, making the role of the elder synonymous with leadership itself. The process of selecting elders is typically based on their proven ability to mediate disputes and lead effectively. As custodians of clan interests and as representatives of their communities, their perspectives carry substantial weight in decision-making processes.
Conflict Resolution and Mediation
One of the most critical roles that elders have historically held is that of conflict resolution. Serving as mediators, they are tasked with resolving disputes within and between clans through the application of traditional justice systems. The approach they employ relies heavily on negotiation and consensus-building. This method of fostering peace emphasizes dialogue over violence, ensuring that resolutions are not only reached but also respected and sustained. Through their deep understanding of tribal laws and customs, elders guide these mediations, acting as both arbitrators and counselors. Their expertise ensures that solutions are in harmony with established customs and cultural principles.
Safeguarding Cultural Practices
Besides their roles in governance, elders are equally vital in the preservation of cultural heritage. The rich oral traditions of Somaliland, encompassing histories, poetry, and values, owe their continuity to the efforts of these elders. By passing down these narratives and traditions, they play a significant role in strengthening the cultural identity of younger generations. This process of knowledge transmission is crucial for preserving the distinct cultural tapestry that characterizes the region. By mentoring and teaching these practices, elders help ensure that the region’s history and values remain vibrant and influential in contemporary times.
Role in Political Systems
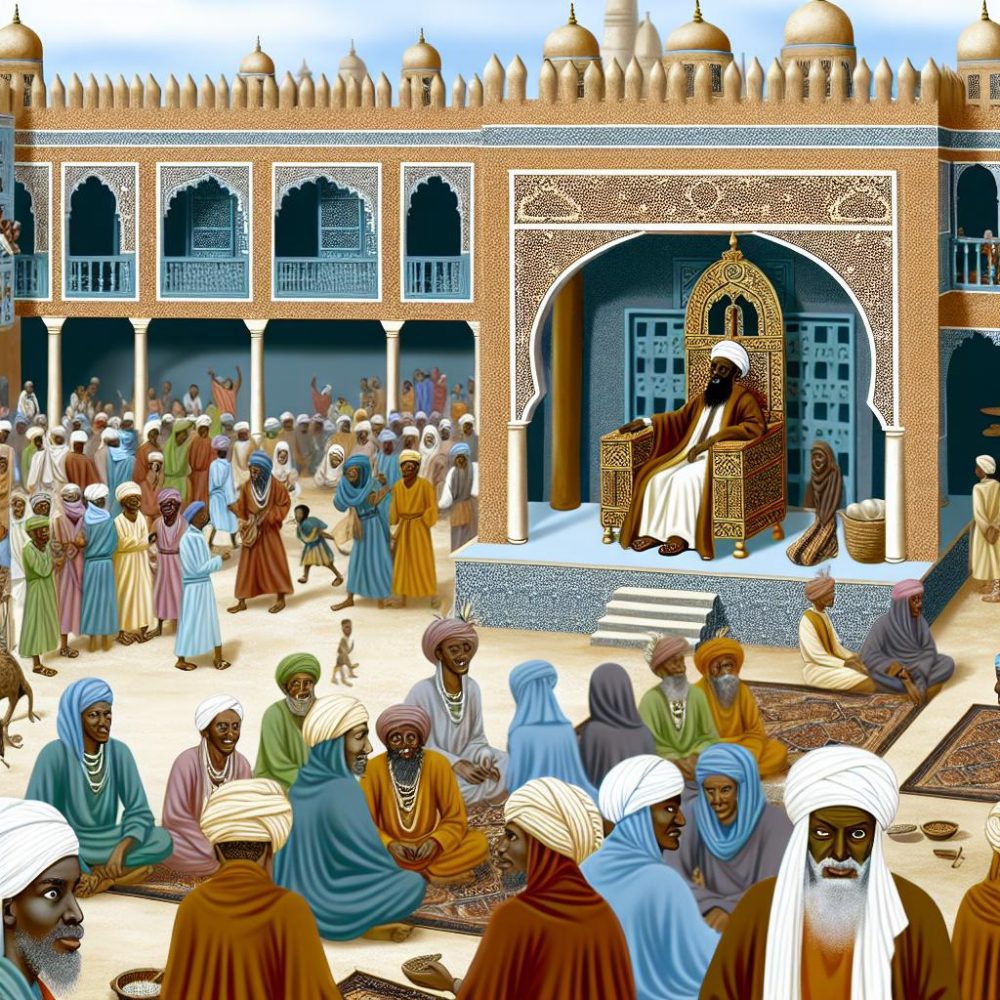
In historical Somaliland, elders have been deeply involved in shaping political frameworks. While modern political structures have since emerged, many foundational principles remain firmly rooted in traditional systems. Elders often provide counsel and offer insights to political leaders, integrating tribal and regional perspectives into broader governance. This ensures that decisions are not made in isolation but rather are reflective of the community’s needs and diverse viewpoints. By blending traditional approaches with current political requirements, elders have helped maintain a balance between innovation and tradition, ensuring that both local and regional considerations are duly taken into account.
Education and Social Responsibility
Elders in historical Somaliland are also viewed as prominent educators and role models. Entrusted with imparting essential life skills and ethical teachings, they guide the youth towards socially responsible adulthood. By teaching moral and ethical values, they contribute significantly to building cohesive societies, where respect, accountability, and communal responsibility are upheld. Their guidance transcends academic or vocational education; it encompasses a broader responsibility to instill values that promote harmony and coexistence. As mentors, they teach patience, resilience, and adaptability—qualities necessary for thriving in both personal and communal settings.
Contemporary Relevance
Despite the evolution of political systems in modern Somaliland, the role of elders continues to hold enormous significance. While reforms and modern governance structures have been introduced, elders still exert influence across numerous aspects of life. Their involvement remains a cornerstone in the preservation of traditional values, ensuring that these coexist alongside modern advancements. This fusion of the old and new creates a dynamic cultural landscape, where the wisdom of the past informs current practices and policies. The continued reverence for elders’ insights reflects the enduring value placed upon their contributions, making them integral to both heritage preservation and contemporary society.
For further exploration of the historical roles of elders in Somaliland, engaging with academic or historical texts from reliable sources can provide a more nuanced understanding. These sources offer comprehensive insights, detailing the various ways in which elders have shaped and continue to influence the socio-cultural and political realms of Somaliland.