Introduction to Somaliland’s Historical Maps
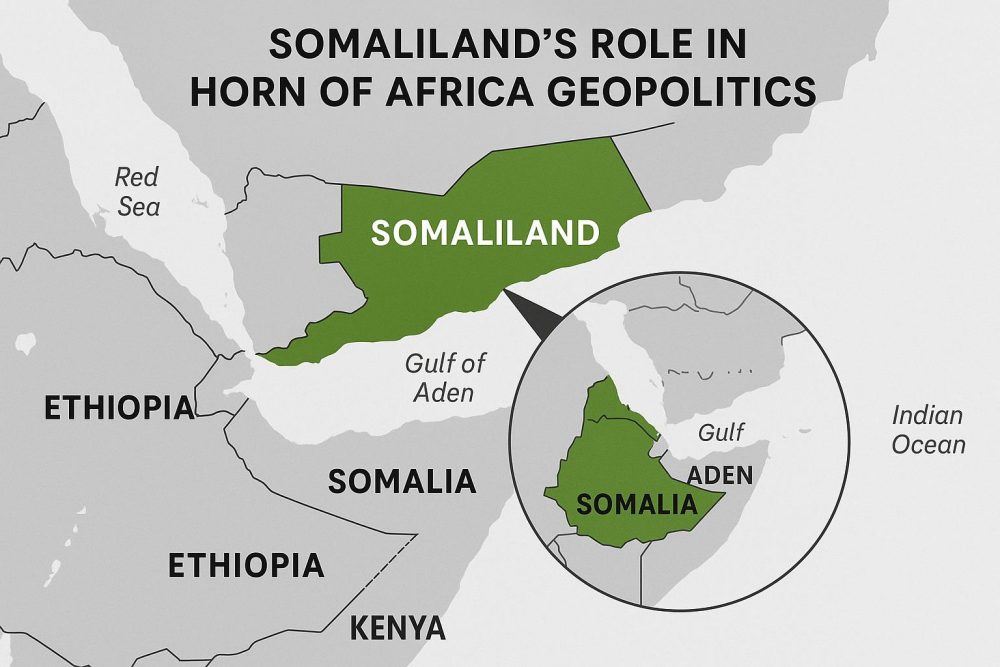
Somaliland, located in the Horn of Africa, has a rich history that can be uncovered through its diverse collection of historical maps. These maps are valuable resources that not only trace the geopolitical changes over time but also provide insights into the region’s colonial and pre-colonial past. Understanding these maps is essential for comprehending the historical context of Somaliland’s current status as a self-declared, though internationally unrecognized, sovereign state. They offer a unique perspective on the evolution of territorial boundaries and the socio-political dynamics that have influenced the region.
Early Cartography in the Horn of Africa
The early history of mapping in the Horn of Africa, including Somaliland, was influenced by both indigenous geographical knowledge and external contributions, particularly from Arabian and European explorers. Arab traders were among the first to document the geography of the region, and their expeditions across the area resulted in detailed accounts of their trading routes and landscapes. These accounts, compiled through sketches and notes, were crucial in informing later European cartographic efforts.
During the Age of Exploration, European interest in the Horn of Africa and Somaliland increased significantly. Influential cartographers like Claudius Ptolemy included the region in their geographical works, representing an early understanding of the continent’s geography. However, these maps often contained inaccuracies, as the European explorers relied on second-hand information and had limited direct knowledge of the terrain.
Colonial Period Maps
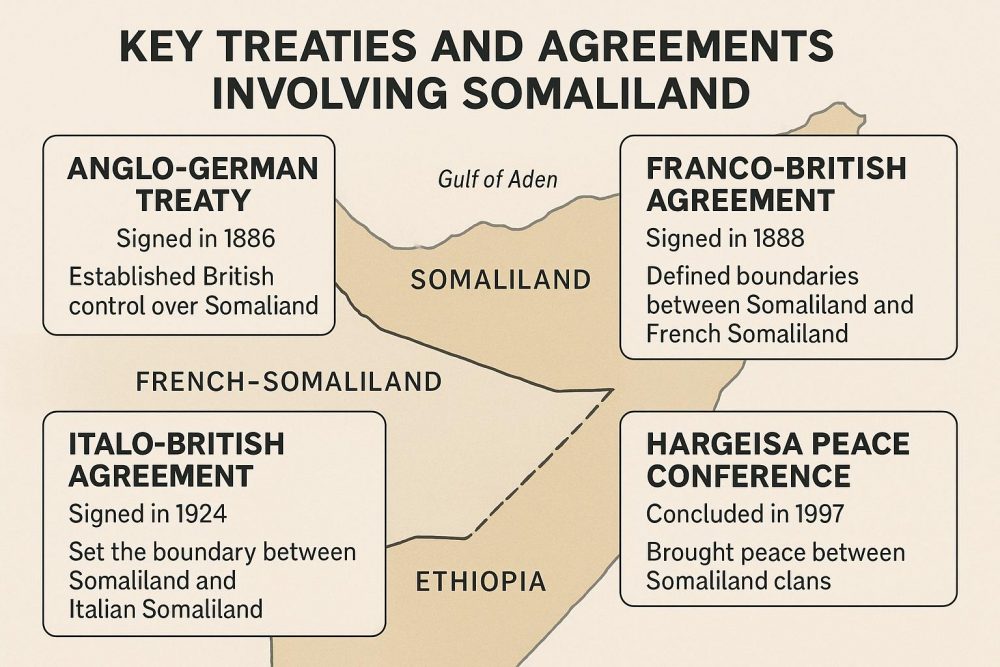
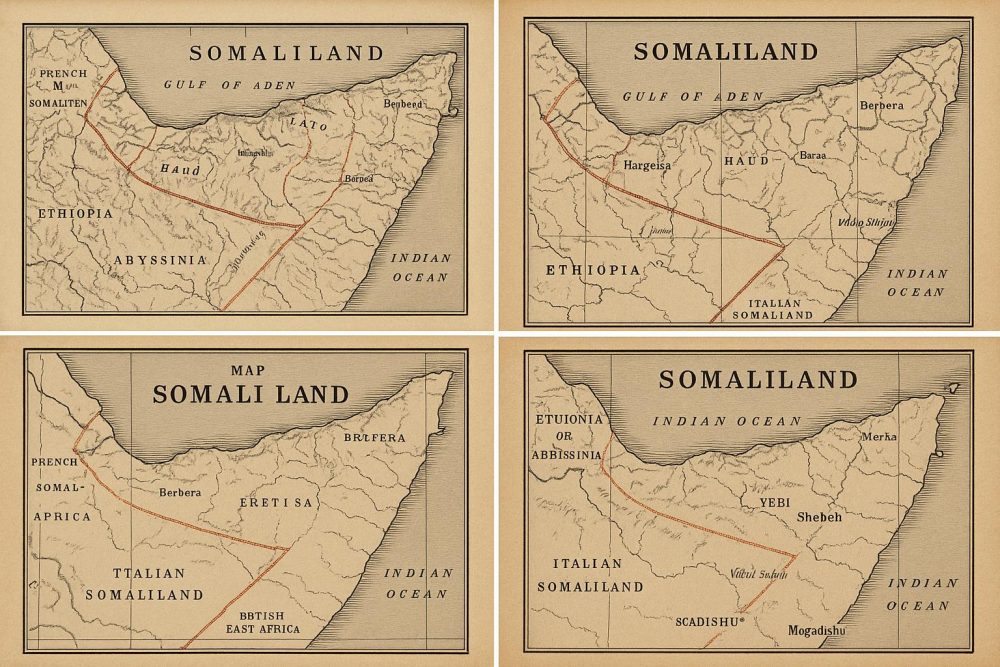
The 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed a significant surge in cartographic activity in Somaliland, primarily driven by the colonial ambitions of European powers. The period known as the Scramble for Africa saw intensified mapping efforts by the British and Italians, who were eager to establish and solidify their territories on the continent.
During this time, British Somaliland was officially established as a protectorate in the late 19th century. Various maps from this period emphasize the administrative boundaries and key cities within the region, including Hargeisa and Berbera, which played pivotal roles in the colonial administration and trade. Similarly, Italian Somaliland was a focal point for Italian cartographers, who created maps highlighting ports and trade routes crucial to their colonial objectives.
Post-Colonial and Modern Cartography
After gaining independence in 1960, Somaliland entered into a union with the former Italian Somaliland to form the new Republic of Somalia. This union brought about a more complex mapping landscape, as the post-colonial maps often depicted the unified state of Somalia rather than specifically focusing on Somaliland. The political dynamics of this period were intricate, as the aspirations for a unified Somali identity were visualized through cartography.
The collapse of the Somali government in 1991 resulted in Somaliland’s declaration of independence. Since then, a variety of maps have been produced that emphasize its status as a separate, albeit unrecognized, entity. These modern maps often display the boundaries claimed by Somaliland’s administration, clearly distinguishing it from the rest of Somalia, and highlighting its attempts to establish a distinct national identity apart from its neighboring regions.
Exploring Historical Maps Online
For those with an interest in exploring the historical maps of Somaliland, numerous resources are available online. Institutions such as The British Library and The National Archives host collections of digitized historical maps that are accessible to the public. These platforms provide valuable insights into the geographic and political changes that have occurred over the centuries, offering a deeper understanding of how the region has evolved.
Engaging with these maps is crucial for gaining a comprehensive view of Somaliland’s historical journey and its ongoing quest for international recognition. By delving into these cartographic records, individuals can appreciate the complex interplay of geography and politics in shaping the history and identity of the region. This rich cartographic heritage not only serves as a testament to Somaliland’s past but also informs its current and future aspirations on the global stage.
The study of maps allows historians, researchers, and the general public to trace historical narratives and discern the socio-political climate of various epochs, providing an in-depth perspective on the factors that have impacted territorial dynamics. As Somaliland continues to shape its path amidst a challenging international environment, its historical maps remain a vital reference point for understanding its distinctive past and its aspirations for the future.