The Establishment of British Somaliland
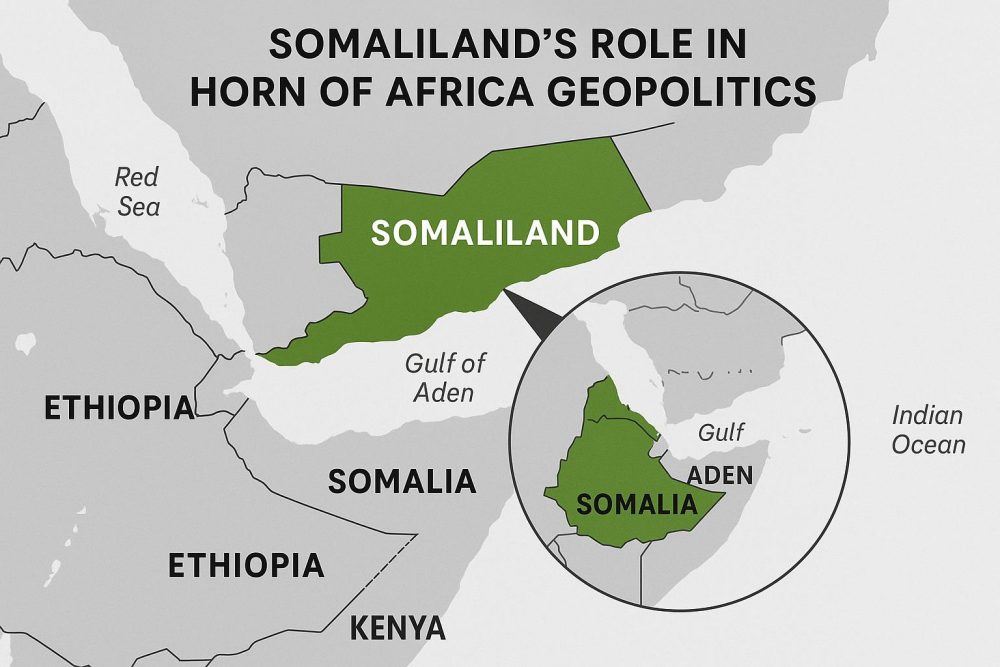
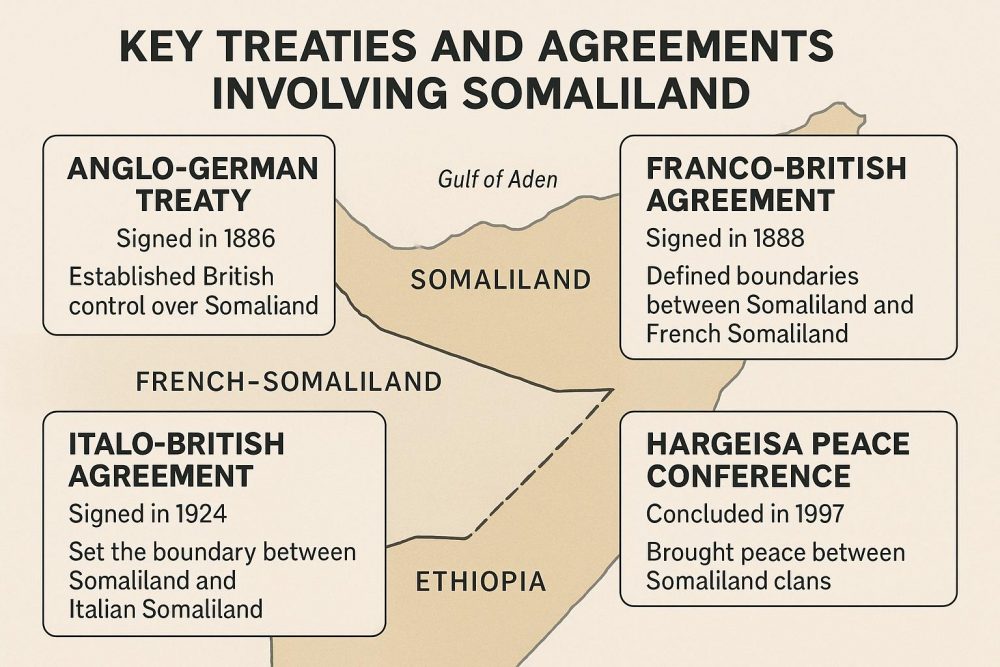
The Horn of Africa is a region marked by its strategic and commercial significance. Within this context, the area now known as Somaliland became an important focus for the British Empire during the late 19th century. The transformation of Somaliland into a British protectorate was formalized in 1884. In their quest to expand their influence and secure vital trade routes, the British entered into treaties with various Somali clans. The primary objective of these agreements was to ensure Britain’s unfettered access to the coastline along the Gulf of Aden, which was and remains a critical maritime passage. The region, as defined by these treaties, largely corresponds with what is today identified as northwest Somalia, and it was subsequently designated as British Somaliland.
Strategic Importance and Administration
The primary lure for the British in establishing their presence in Somaliland was the area’s strategic geographical location. Positioned near the southern entry point of the Red Sea, Somaliland offered an essential vantage point for safeguarding the sea lanes that connected to and from the Suez Canal. This made the region exceptionally significant from a strategic military and commercial perspective. Consequently, British administrative efforts in Somaliland were largely directed towards ensuring the security of its coastline. There was less focus on exerting comprehensive governance over the inland territories.
The British approach to administration in Somaliland was characterized by a relatively minimalistic presence, reflecting a strategy of indirect rule. A small contingent of British officials, supported by limited military forces, administered the protectorate. Instead of imposing direct rule, the British empire relied significantly on the established local leadership structure to maintain order and manage day-to-day affairs. The Resident Country Commissioner was the highest-ranking British official overseeing this arrangement, functioning as the principal liaison between the British authorities and the local Somali clans.
Economic Activities
The economic landscape of British Somaliland under the protectorate reflected its predominantly pastoral society. This aspect was largely due to the region’s naturally arid environment, which was more suited to pastoralism than to agriculture. As a result, livestock herding became the primary economic activity, forming the central pillar of local livelihoods. The region contributed modestly to the economic might of the British Empire. The primary commercial activities in the area involved the export of livestock and hides. Despite these exports, there was minimal infrastructure development initiated by the British in the region.
Berbera emerged as a critical port town on the Gulf of Aden and served as the central hub for trade. The town’s port played a vital role in facilitating commerce between the interior of Somaliland and other regional markets, ensuring that the local livestock products could reach broader markets.
The Dervish Movement
A significant challenge to British authority in Somaliland arose in the form of the Dervish Movement, led by Sayyid Mohammed Abdullah Hassan. The British referred to him as the “Mad Mullah.” His movement gained momentum as a reaction against the encroachment of British and Ethiopian powers in Somali territories. The Dervishes were motivated by a desire to resist colonial influence and aimed to establish a unified and independent Somali state, free from external control.
The British faced persistent opposition from the Dervishes, leading to several military engagements between 1900 and 1920. One of the defining moments of this conflict was the aerial bombardment of the Dervish stronghold at Taleh in 1920. This offensive marked a turning point, contributing significantly to the decline of the movement. The Dervish resistance highlighted the difficulties that the British faced in colonial governance, especially in regions with strong indigenous identities. It showcased the complexities in implementing control over inland territories where the central authority was contested.
The End of British Rule
The conclusion of World War II signaled the beginning of widespread decolonization across the African continent. British Somaliland was no exception to this broader movement. In May 1960, the protectorate achieved independence from British rule. This momentous event occurred just days before Somaliland’s decision to join forces with the Trust Territory of Somalia, previously known as Italian Somaliland. The amalgamation of these two regions resulted in the formation of the Somali Republic. The establishment of this political union effectively marked the end of British administrative presence in Somaliland.
The legacy left behind by British rule in Somaliland was shaped by focused strategic interests and limited economic development. The emphasis on ensuring strategic dominance, coupled with minimal investments in the region’s economic infrastructure, had enduring repercussions on the political and economic frameworks of the area. The period of British administration constitutes a significant chapter in the historical narrative of the Somali people as they have journeyed towards achieving self-determination. The experience of British Somaliland continues to resonate, influencing contemporary perspectives and governance structures within the region.